단일 소스 최단 경로 알고리즘(임의 가중치 양수 또는 음수)은 Bellman-Ford 알고리즘도 알려져 있습니다. 소스 정점에서 다른 정점까지의 최소 거리를 찾는 데 사용됩니다. 이 알고리즘과 Dijkstra 알고리즘의 주요 차이점은 Dijkstra 알고리즘에서는 음수 가중치를 처리할 수 없지만 여기서는 쉽게 처리할 수 있다는 것입니다.
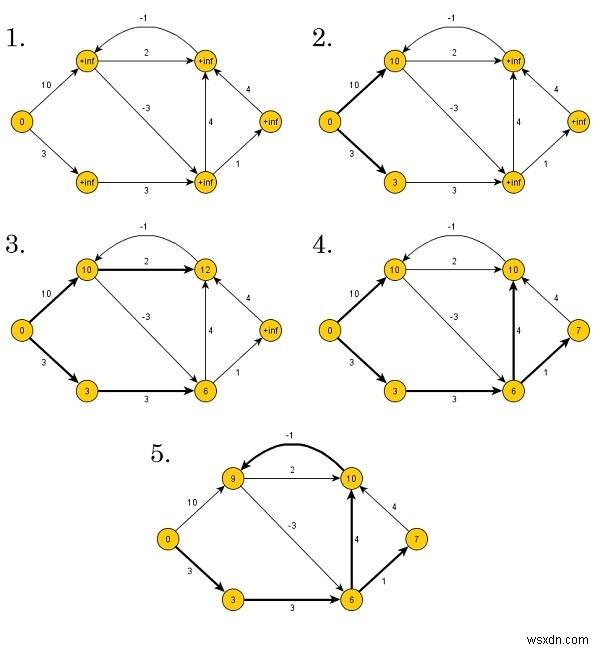
Bellman-Ford 알고리즘은 상향식으로 거리를 찾습니다. 처음에는 경로에 가장자리가 하나만 있는 거리를 찾습니다. 그런 다음 가능한 모든 솔루션을 찾기 위해 경로 길이를 늘립니다.
입력 − 그래프의 비용 매트릭스:
0 6 ∞ 7 ∞ ∞ 0 5 8 -4 ∞ -2 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ -3 0 9 2 ∞ 7 ∞ 0
출력 - 소스 정점:2
수직:0 1 2 3 4
거리:-4 -2 0 3 -6
이전:4 2 -1 0 1
그래프에는 음의 에지 사이클이 없습니다.
알고리즘
bellmanFord(dist, pred, 소스)
입력 − 거리 목록, 선행자 목록 및 원본 정점.
출력 − 음의 주기가 발견되면 참입니다.
Begin iCount := 1 maxEdge := n * (n - 1) / 2 //n is number of vertices for all vertices v of the graph, do dist[v] := ∞ pred[v] := ϕ done dist[source] := 0 eCount := number of edges present in the graph create edge list named edgeList while iCount < n, do for i := 0 to eCount, do if dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i) dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i) pred[edgeList[i].v] := edgeList[i].u done done iCount := iCount + 1 for all vertices i in the graph, do if dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + (cost[u,v] for edge i), then return true done return false End
예시(C++)
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#define V 5
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph (directed) vertex 5
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 6, INF, 7, INF},
{INF, 0, 5, 8, -4},
{INF, -2, 0, INF, INF},
{INF, INF, -3, 0, 9},
{2, INF, 7, INF, 0}
};
typedef struct{
int u, v, cost;
}edge;
int isDiagraph(){
//check the graph is directed graph or not
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<V; i++){
for(j = 0; j<V; j++){
if(costMat[i][j] != costMat[j][i]){
return 1;//graph is directed
}
}
}
return 0;//graph is undirected
}
int makeEdgeList(edge *eList){
//create edgelist from the edges of graph
int count = -1;
if(isDiagraph()){
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<V; j++){
if(costMat[i][j] != 0 && costMat[i][j] != INF){
count++;//edge find when graph is directed
eList[count].u = i; eList[count].v = j;
eList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
}
}
}else{
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++){
for(int j = 0; j<i; j++){
if(costMat[i][j] != INF){
count++;//edge find when graph is undirected
eList[count].u = i; eList[count].v = j;
eList[count].cost = costMat[i][j];
}
}
}
}
return count+1;
}
int bellmanFord(int *dist, int *pred,int src){
int icount = 1, ecount, max = V*(V-1)/2;
edge edgeList[max];
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++){
dist[i] = INF;//initialize with infinity
pred[i] = -1;//no predecessor found.
}
dist[src] = 0;//for starting vertex, distance is 0
ecount = makeEdgeList(edgeList); //edgeList formation
while(icount < V){ //number of iteration is (Vertex - 1)
for(int i = 0; i<ecount; i++){
if(dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v]){
//relax edge and set predecessor
dist[edgeList[i].v] = dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v];
pred[edgeList[i].v] = edgeList[i].u;
}
}
icount++;
}
//test for negative cycle
for(int i = 0; i<ecount; i++){
if(dist[edgeList[i].v] > dist[edgeList[i].u] + costMat[edgeList[i].u][edgeList[i].v]){
return 1;//indicates the graph has negative cycle
}
}
return 0;//no negative cycle
}
void display(int *dist, int *pred){
cout << "Vert: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout <<setw(3) << i << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Dist: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout << setw(3) << dist[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "Pred: ";
for(int i = 0; i<V; i++)
cout << setw(3) << pred[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main(){
int dist[V], pred[V], source, report;
source = 2;
report = bellmanFord(dist, pred, source);
cout << "Source Vertex: " << source<<endl;
display(dist, pred);
if(report)
cout << "The graph has a negative edge cycle" << endl;
else
cout << "The graph has no negative edge cycle" << endl;
} 출력
Source Vertex: 2 Vert: 0 1 2 3 4 Dist: -4 -2 0 3 -6 Pred: 4 2 -1 0 1 The graph has no negative edge cycle
