무방향 그래프의 경우 정점 덮개는 정점의 하위 집합이며 그래프의 모든 모서리(u, v)에 대해 u 또는 v가 집합에 있습니다.
이진 트리를 사용하면 정점 덮개 문제를 쉽게 해결할 수 있습니다.
이 문제는 두 개의 하위 문제로 나눌 수 있습니다. 루트가 정점 덮개의 일부인 경우. 이 경우 루트는 모든 자식 가장자리를 덮습니다. 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 하위 트리의 꼭짓점 덮개 크기를 찾고 루트에 1을 더하면 됩니다.
입력 및 출력
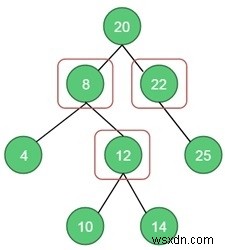
Input: A binary tree.Output: The vertex cover is 3.
알고리즘
vertexCover(root node)
이 문제에서는 하나의 이진 트리가 형성되고 각 노드는 해당 노드가 포함하는 데이터와 정점 수를 보유합니다.
입력 - 바이너리 트리의 루트입니다.
출력 - 루트로 덮인 정점의 수입니다.
Begin if root is φ, then return 0 if root has no child, then return 0 if vCover(root) ≠ 0, then return vCover(root) withRoot := 1 + vertexCover(left(root)) + vertexCover(right(root)) withoutRoot := 0 if root has left child, then withoutRoot := withoutRoot + vertexCover(left(left(root))) + vertexCover(left(right(root))) if root has right child, then withoutRoot := withoutRoot + vertexCover(right(left(root))) + vertexCover(right(right(root))) return vCover(root) End
예시
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int vCover;
node *left, *right;
};
node *getNode(int data) {
node *newNode = new (node);
newNode->data = data;
newNode->vCover = 0; //set vertex cover to 0
newNode->left = NULL;
newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode; //newly created node
}
int vertexCover(node *root) {
if(root == NULL) //when tree is empty
return 0;
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) //when no other edge from root
return 0;
if(root->vCover != 0) //when vertex cover of this node is found, leave that node
return root->vCover;
int sizeWithRoot = 1 + vertexCover(root->left) + vertexCover(root->right);
int sizeWithOutRoot = 0;
if(root->left != NULL) //when root is not included and go for left child
sizeWithOutRoot += 1 + vertexCover(root->left->left) + vertexCover(root->left->right);
if(root->right != NULL) //when root is not included and go for right child
sizeWithOutRoot += 1 + vertexCover(root->right->left) + vertexCover(root->right->right);
root->vCover = (sizeWithRoot < sizeWithOutRoot)?sizeWithRoot:sizeWithOutRoot; //minimum vertex cover
return root->vCover;
}
int main() {
//create tree to check vertex cover
node *root = getNode(20);
root->left = getNode(8); root->right = getNode(22);
root->left->left = getNode(4); root->left->right = getNode(12);
root->left->right->left = getNode(10); root->left->right->right = getNode(14);
root->right->right = getNode(25);
cout << "Minimal vertex cover: " << vertexCover(root);
} 출력
Minimal vertex cover: 3