오일러 경로는 모든 모서리를 정확히 한 번만 방문할 수 있는 경로입니다. 같은 정점을 여러 번 사용할 수 있습니다. 오일러 회로는 특수한 유형의 오일러 경로입니다. 오일러 경로의 시작 꼭짓점과 해당 경로의 끝 꼭짓점이 연결되어 있는 경우 이를 오일러 회로라고 합니다.
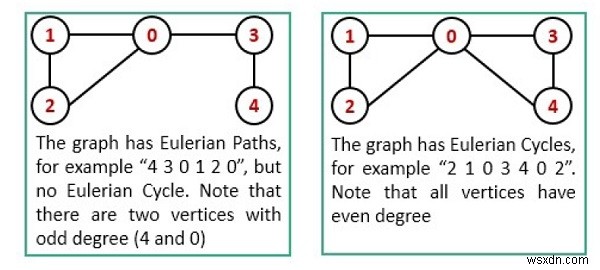
경로와 회로를 감지하려면 다음 조건을 따라야 합니다.
- 그래프가 연결되어 있어야 합니다.
- 정확히 두 개의 정점이 홀수 차수를 가질 때 오일러 경로입니다.
- 무방향 그래프의 정점이 홀수 차수를 가지지 않으면 오일러 회로입니다.
입력 및 출력
Input: Adjacency matrix of a graph. 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 Output: The graph has an Eulerian path.
알고리즘
traverse(u, 방문)
입력: 시작 노드 u와 방문한 노드를 표시하여 방문한 노드를 표시합니다.
출력 - 연결된 모든 정점을 순회합니다.
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End
연결됨(그래프)
입력 - 그래프.
출력 - 그래프가 연결되어 있으면 참입니다.
Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
isEulerian(그래프)
입력 - 주어진 그래프.
출력 - 오일러 경로가 없으면 0, 오일러 경로가 있으면 1, 오일러 회로가 발견되면 2를 반환합니다.
Begin if isConnected() is false, then return false define list of degree for each node oddDegree := 0 for all vertex i in the graph, do for all vertex j which are connected with i, do increase degree done if degree of vertex i is odd, then increase dooDegree done if oddDegree > 2, then return 0 if oddDegree = 0, then return 2 else return 1 End
예시
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
/* int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
*/ //uncomment to check Euler Circuit
/* int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
*/ //Uncomment to check Non Eulerian Graph
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v])
traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++) {
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int isEulerian() {
if(isConnected() == false) //when graph is not connected
return 0;
vector<int> degree(NODE, 0);
int oddDegree = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
if(graph[i][j])
degree[i]++; //increase degree, when connected edge found
}
if(degree[i] % 2 != 0) //when degree of vertices are odd
oddDegree++; //count odd degree vertices
}
if(oddDegree > 2) //when vertices with odd degree greater than 2
return 0;
return (oddDegree)?1:2; //when oddDegree is 0, it is Euler circuit, and when 2, it is Euler path
}
int main() {
int check;
check = isEulerian();
switch(check) {
case 0: cout << "The graph is not an Eulerian graph.";
break;
case 1: cout << "The graph has an Eulerian path.";
break;
case 2: cout << "The graph has a Eulerian circuit.";
break;
}
} 출력
The graph has an Eulerian path.
