가중된 방향성 비순환 그래프 하나가 제공됩니다. 다른 소스 정점도 제공됩니다. 이제 그래프에서 시작 노드에서 다른 모든 정점까지의 최단 거리를 찾아야 합니다.
더 작은 거리를 감지하기 위해 음수 가중치 그래프에 Bellman-Ford와 같은 다른 알고리즘을 사용할 수 있습니다. 양수 가중치의 경우 Dijkstra 알고리즘도 도움이 됩니다. Directed Acyclic Graph의 경우 토폴로지 정렬 기술을 사용하여 복잡성을 줄입니다.
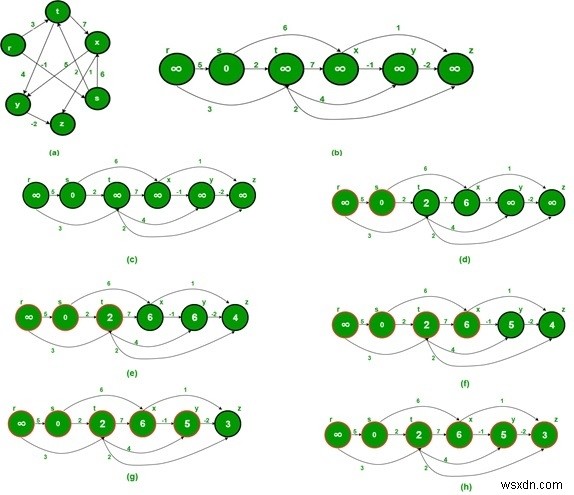
입력 및 출력
Input: The cost matrix of the graph. 0 5 3 -∞ -∞ -∞ -∞ 0 2 6 -∞ -∞ -∞ -∞ 0 7 4 2 -∞ -∞ -∞ 0 -1 1 -∞ -∞ -∞ -∞ 0 -2 -∞ -∞ -∞ -∞ -∞ 0 Output: Shortest Distance from Source Vertex 1 Infinity 0 2 6 5 3
알고리즘
topoSort(u, 방문, 스택)
입력 :시작 노드 u, 추적할 방문 목록, 스택.
출력: 토폴로지 방식으로 노드를 정렬합니다.
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, which is connected with u, do if v is not visited, then topoSort(v, visited, stack) done push u into the stack End
shortestPath(시작)
입력 - 시작 노드입니다.
출력 - 시작 노드에서 모든 정점의 최단 거리 목록입니다.
Begin initially make all nodes as unvisited for each node i, in the graph, do if i is not visited, then topoSort(i, visited, stack) done make distance of all vertices as ∞ dist[start] := 0 while stack is not empty, do pop stack item and take into nextVert if dist[nextVert] ≠∞, then for each vertices v, which is adjacent with nextVert, do if cost[nextVert, v] ≠∞, then if dist[v] > dist[nectVert] + cost[nextVert, v], then dist[v] := dist[nectVert] + cost[nextVert, v] done done for all vertices i in the graph, do if dist[i] = ∞, then display Infinity else display dist[i] done End
예시
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#define NODE 6
#define INF 9999
using namespace std;
int cost[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 5, 3, INF, INF, INF},
{INF, 0, 2, 6, INF, INF},
{INF, INF, 0, 7, 4, 2},
{INF, INF, INF, 0, -1, 1},
{INF, INF, INF, INF, 0, -2},
{INF, INF, INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
void topoSort(int u, bool visited[], stack<int>&stk) {
visited[u] = true; //set as the node v is visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(cost[u][v]) { //for allvertices v adjacent to u
if(!visited[v])
topoSort(v, visited, stk);
}
}
stk.push(u); //push starting vertex into the stack
}
void shortestPath(int start) {
stack<int> stk;
int dist[NODE];
bool vis[NODE];
for(int i = 0; i<NODE;i++)
vis[i] = false; // make all nodes as unvisited at first
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) //perform topological sort for vertices
if(!vis[i])
topoSort(i, vis, stk);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
dist[i] = INF; //initially all distances are infinity
dist[start] = 0; //distance for start vertex is 0
while(!stk.empty()) { //when stack contains element, process in topological order
int nextVert = stk.top(); stk.pop();
if(dist[nextVert] != INF) {
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(cost[nextVert][v] && cost[nextVert][v] != INF){ if(dist[v] > dist[nextVert] +cost[nextVert][v])dist[v] = dist[nextVert] + cost[nextVert][v];
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
(dist[i] == INF)?cout << "Infinity ":cout << dist[i]<<" ";
}
main() {
int start = 1;
cout << "Shortest Distance From Source Vertex "<<start<<endl;
shortestPath(start);
} 출력
Shortest Distance From Source Vertex 1 Infinity 0 2 6 5 3
