여기서 B-Tree에서 노드를 삭제하는 방법을 살펴보겠습니다. 아래와 같은 BTree가 있다고 가정합니다 -
B-트리의 예 -
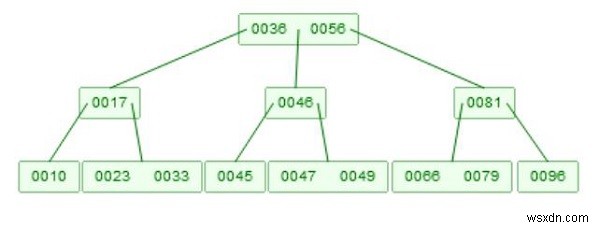
삭제에는 두 부분이 있습니다. 먼저 요소를 찾아야 합니다. 그 전략은 쿼리와 같습니다. 이제 삭제를 위해 몇 가지 규칙에 주의해야 합니다. 하나의 노드에는 최소 m/2개의 요소가 있어야 합니다. 따라서 하나의 요소를 삭제하고 m-1개 미만의 요소가 남아 있으면 자동으로 조정됩니다. 전체 노드가 삭제되면 자식 노드가 병합되고 크기가 m과 같으면 두 부분으로 나누면 다시 중앙값이 올라갑니다.
46을 삭제한다고 가정합니다. 이제 두 개의 자식이 있습니다. [45], [47, 49], [45, 47, 49]가 합쳐지면 47이 올라갑니다.
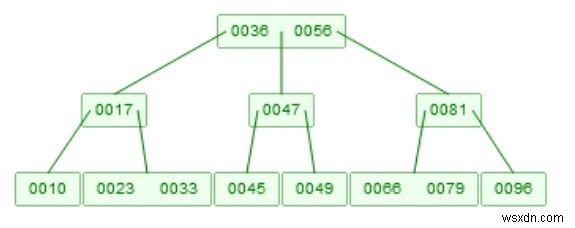
알고리즘
BTreeDelete(x, 키) −
입력 − 트리의 루트, 삭제할 키
키가 목록에 있다고 가정합니다.
if x is leaf, then delete object with key ‘key’ from x else if x does not contain the object with key ‘key’, then locate the child x->child[i] whose key range is holding ‘key’ y := x->child[i] if y has m/2 elements, then If the sibling node z immediate to the left or right of y, has at least one more object than m/2, add one more object by moving x->key[i] from x to y, and move that last or first object from z to x. If y is non-leaf node, then last or first child pointer in z is also moved to y else any immediate sibling of y has m/2 elements, merge y with immediate sibling end if BTreeDelete(y, key) else if y that precedes ‘key’ in x, has at-least m/2 + 1 objects, then find predecessor k of ‘key’, in the sub-tree rooted by y. then recursively delete k from the sub-tree and replace key with k in x else if ys has m/2 elements, then check the child z, which is immediately follows ‘key’ in x if z has at least m/2+1 elements, then find successor k of ‘key’, in the sub-tree rooted by z. recursively delete k from sub-tree, and replace key with k in x else both y and z has m/2 elements, then merge then into one node, and push ‘key’ down to the new node as well. Recursively delete ‘key’ from this new node end if end if
