연결된 그래프 G(V,E)가 있고 모든 간선에 대한 가중치 또는 비용이 제공됩니다. Prim의 알고리즘은 그래프 G에서 최소 스패닝 트리를 찾습니다.
그것은 성장 나무 접근입니다. 이 알고리즘은 트리를 시작하기 위해 시드 값이 필요합니다. 시드 정점이 성장하여 전체 트리를 형성합니다.
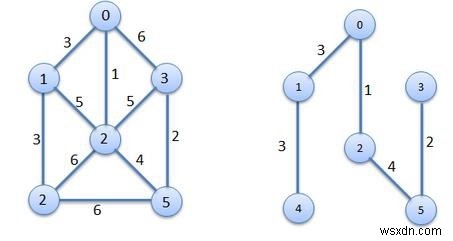
문제는 두 세트를 사용하여 해결됩니다. 한 세트는 이미 선택된 노드를 보유하고 다른 세트는 아직 고려되지 않은 항목을 보유합니다. seed vertex에서 최소 edge cost를 기준으로 인접한 vertex를 취하므로 노드를 하나씩 취하여 트리를 성장시킵니다.
-
이 문제의 시간 복잡도는 O(V2)입니다. 여기서 V는 정점의 수입니다.
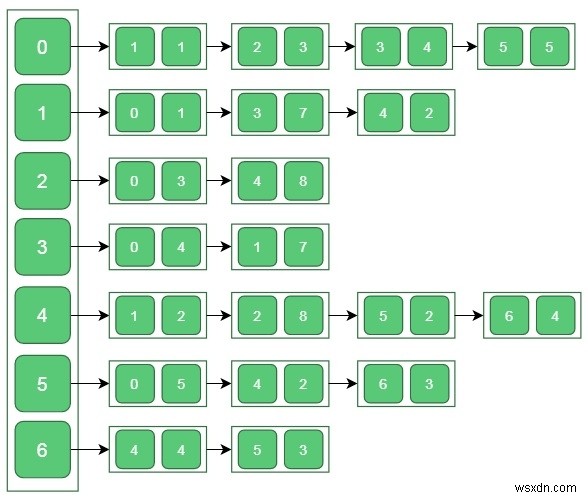
입력 − 인접 목록 −
출력 -
(0)---(1|1) (0)---(2|3) (0)---(3|4) (1)---(0|1) (1)---(4|2) (2)---(0|3) (3)---(0|4) (4)---(1|2) (4)---(5|2) (5)---(4|2) (5)---(6|3) (6)---(5|3)
알고리즘
prims(g:그래프, t:트리, 시작)
입력 − 그래프 g, 빈 트리 및 'start'라는 이름의 시드 정점 출력:가장자리를 추가한 후의 트리.
Begin define two sets as usedVert, unusedVert usedVert[0] := start and unusedVert[0] := φ for all vertices except start do usedVert[i] := φ unusedVert[i] := i //add all vertices in unused list done while number of vertices in usedVert ≠ V do //V is number of total nodes min := ∞ for all vertices of usedVert array do for all vertices of the graph do if min > cost[i,j] AND i ≠ j then min := cost[i,j] ed := edge between i and j, and cost of ed := min done done unusedVert[destination of ed] := φ add edge ed into the tree t add source of ed into usedVert done End
예시(C++)
#include<iostream>
#define V 7
#define INF 999
using namespace std;
//Cost matrix of the graph
int costMat[V][V] = {
{0, 1, 3, 4, INF, 5, INF},
{1, 0, INF, 7, 2, INF, INF},
{3, INF, 0, INF, 8, INF, INF},
{4, 7, INF, 0, INF, INF, INF},
{INF, 2, 8, INF, 0, 2, 4},
{5, INF, INF, INF, 2, 0, 3},
{INF, INF, INF, INF, 4, 3, 0}
};
typedef struct{
int u, v, cost;
}edge;
class Tree{
int n;
edge edges[V-1]; //as a tree has vertex-1 edges
public:
Tree(){
n = 0;
}
void addEdge(edge e){
edges[n] = e; //add edge e into the tree
n++;
}
void printEdges(){ //print edge, cost and total cost
int tCost = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
cout << "Edge: " << char(edges[i].u+'A') < "--" << char(edges[i].v+'A');
cout << " And Cost: " << edges[i].cost << endl;
tCost += edges[i].cost;
}
cout << "Total Cost: " << tCost << endl;
}
friend void prims(Tree &tre, int start);
};
void prims(Tree &tr, int start){
int usedVert[V], unusedVert[V];
int i, j, min, p;
edge ed;
//initialize
usedVert[0] = start; p = 1;
unusedVert[0] = -1;//-1 indicates the place is empty
for(i = 1; i<V; i++){
usedVert[i] = -1;//all places except first is empty
unusedVert[i] = i;//fill with vertices
}
tr.n = 0;
//get edges and add to tree
while(p != V){ //p is number of vertices in usedVert array
min = INF;
for(i = 0; i<p; i++){
for(j = 0; j<V; j++){
if(unusedVert[j] != -1){
if(min > costMat[i][j] && costMat[i][j] != 0){
//find the edge with minimum cost
//such that u is considered and v is not considered yet
min = costMat[i][j];
ed.u = i; ed.v = j; ed.cost = min;
}
}
}
}
unusedVert[ed.v] = -1;//delete v from unusedVertex
tr.addEdge(ed);
usedVert[p] = ed.u; p++;//add u to usedVertex
}
}
main(){
Tree tr;
prims(tr, 0); //starting node 0
tr.printEdges();
} 출력
(0)---(1|1) (0)---(2|3) (0)---(3|4) (1)---(0|1) (1)---(4|2) (2)---(0|3) (3)---(0|4) (4)---(1|2) (4)---(5|2) (5)---(4|2) (5)---(6|3) (6)---(5|3)
